Investigation and Follow Up of Neurological Complications After Surgery for the Parapharyngeal Space Tumors
Background
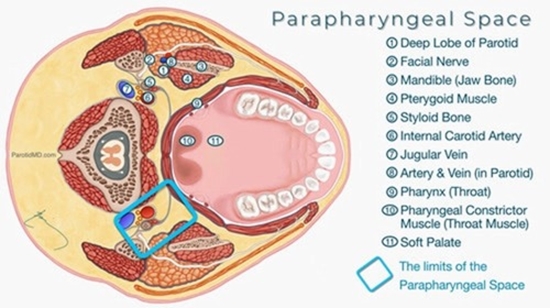
The parapharyngeal space is a deep space located in the neck that extending from the skull base to the hyoid bone. Surgical resection is the primary treatment for PPS masses but challenging due to the presence of vital vascular and neural structures, increasing the risk of postoperative neurological complications such as cranial nerve palsies and first bite syndrome. Neurogenic tumors have a higher likelihood of causing cranial nerve dysfunction compared to non-neurogenic tumors. Understanding the relationship between postoperative neurological complications and the pathological type of PPS masses is essential for optimizing treatment strategies.
Objective
This study aims to assess the neurological complications following surgery for PPS masses and analyze their relationship with the pathological type of the mass.
Materials and Methods
This retrospective cohort study included 90 patients who underwent surgical resection of parapharyngeal space (PPS) masses at Amir Alam Hospital, Tehran, between March 2018 and September 2023. Neurological complications, including vocal cord paralysis, tongue movement disorders, Horner’s syndrome, first bite syndrome, and glossopharyngeal and facial nerve palsies, were assessed at multiple time points (1 month, 6 months, and 1 year) post-surgery. Statistical analyses were performed to determine associations between tumor type and neurological outcomes.
Results
The study found that surgery for PPS tumors frequently led to neurological complications, with vagus nerve palsy and first bite syndrome being the most common. True vocal cord paralysis occurred in 10% of cases within the first year, while first bite syndrome was observed in 20% within 6 months. Peripheral nerve tumors and paragangliomas were significantly associated with higher rates of cranial nerve dysfunction (P < 0.05).
Conclusion
Postoperative neurological complications following PPS tumor resection are common, particularly in neurogenic tumors. The findings emphasize the need for careful preoperative assessment, surgical planning, and patient counseling regarding potential long-term functional deficits






comment